Introducción al algoritmo de ordenación por fusión
Merge sort es un algoritmo de clasificación basado en la técnica "divide y vencerás". Es uno de los algoritmos de clasificación más eficientes.
En este artículo, aprenderá sobre el funcionamiento del algoritmo de clasificación de fusión, el algoritmo de clasificación de fusión, su complejidad temporal y espacial, y su implementación en varios lenguajes de programación como C ++, Python y JavaScript.
¿Cómo funciona el algoritmo de clasificación por fusión?
Merge sort funciona según el principio de divide y vencerás. Merge sort divide repetidamente una matriz en dos subarreglos iguales hasta que cada subarreglo consta de un solo elemento. Finalmente, todos esos subarreglos se combinan de manera que se ordena el arreglo resultante.
Este concepto se puede explicar de manera más eficiente con la ayuda de un ejemplo. Considere una matriz sin clasificar con los siguientes elementos: {16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18}.
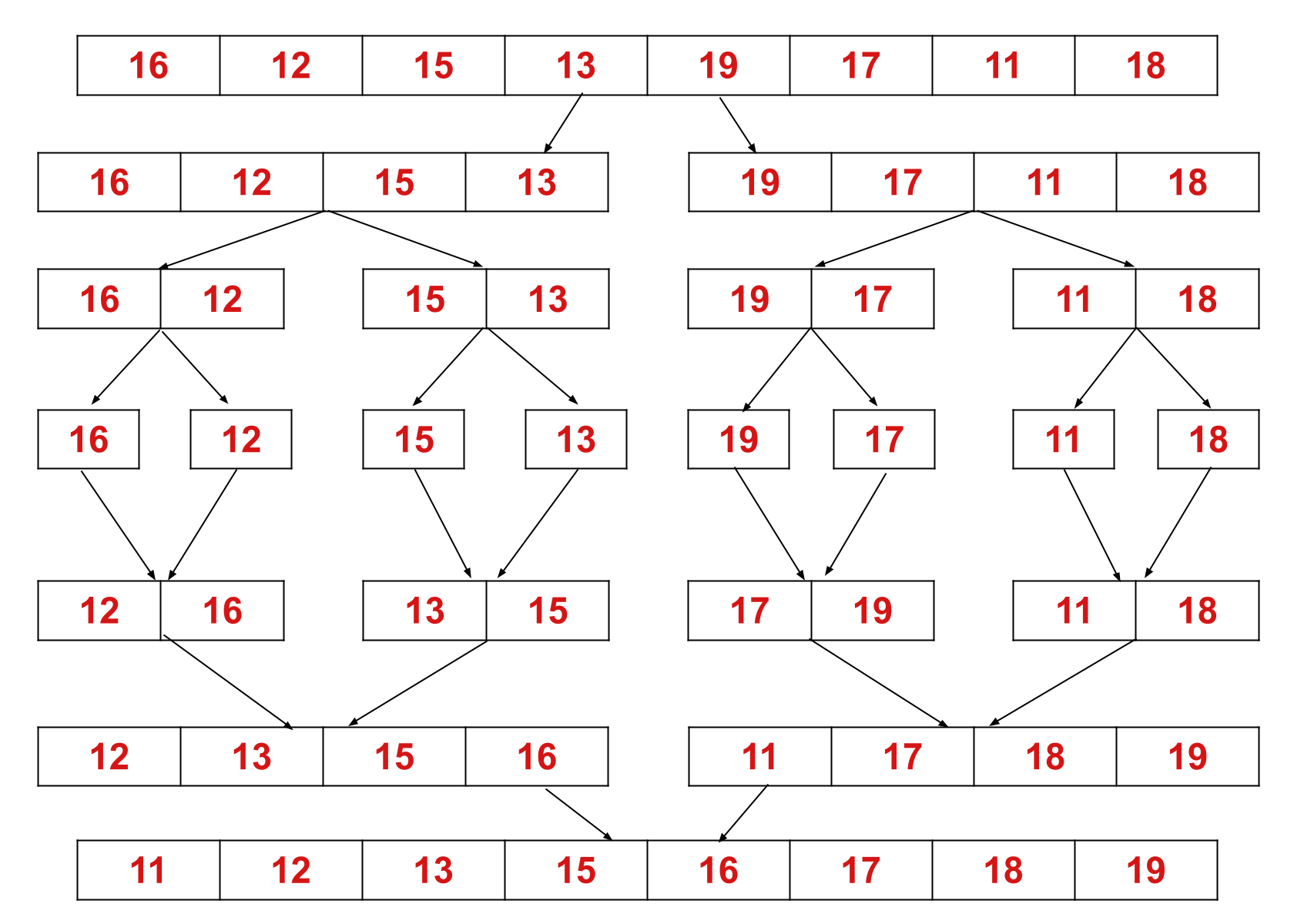
Aquí, el algoritmo de clasificación de combinación divide la matriz en dos mitades, se llama a sí mismo para las dos mitades y luego fusiona las dos mitades ordenadas.
Combinar algoritmo de ordenación
A continuación se muestra el algoritmo del tipo de combinación:
MergeSort(arr[], leftIndex, rightIndex)
if leftIndex >= rightIndex
return
else
Find the middle index that divides the array into two halves:
middleIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex-leftIndex)/2
Call mergeSort() for the first half:
Call mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex)
Call mergeSort() for the second half:
Call mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex)
Merge the two halves sorted in step 2 and 3:
Call merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex)
Complejidad temporal y espacial del algoritmo de clasificación por fusión
El algoritmo de clasificación Merge se puede expresar en forma de la siguiente relación de recurrencia:
T (n) = 2T (n / 2) + O (n)
Después de resolver esta relación de recurrencia utilizando el teorema del maestro o el método del árbol de recurrencia, obtendrá la solución como O (n logn). Por lo tanto, la complejidad de tiempo del algoritmo de clasificación de fusión es O (n logn) .
La complejidad de tiempo en el mejor de los casos del tipo de combinación: O (n logn)
La complejidad del tiempo de caso promedio del tipo de combinación: O (n logn)
La complejidad de tiempo del peor de los casos del tipo de combinación: O (n logn)
La complejidad del espacio auxiliar del algoritmo de clasificación por fusión es O (n) ya que se requiere n espacio auxiliar en la implementación de clasificación por fusión.
Implementación en C ++ del algoritmo de clasificación por fusión
A continuación se muestra la implementación de C ++ del algoritmo de ordenación por combinación:
// C++ implementation of the
// merge sort algorithm
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// This function merges two subarrays of arr[]
// Left subarray: arr[leftIndex..middleIndex]
// Right subarray: arr[middleIndex+1..rightIndex]
void merge(int arr[], int leftIndex, int middleIndex, int rightIndex)
{
int leftSubarraySize = middleIndex - leftIndex + 1;
int rightSubarraySize = rightIndex - middleIndex;
// Create temporary arrays
int L[leftSubarraySize], R[rightSubarraySize];
// Copying data to temporary arrays L[] and R[]
for (int i = 0; i < leftSubarraySize; i++)
L[i] = arr[leftIndex + i];
for (int j = 0; j < rightSubarraySize; j++)
R[j] = arr[middleIndex + 1 + j];
// Merge the temporary arrays back into arr[leftIndex..rightIndex]
// Initial index of Left subarray
int i = 0;
// Initial index of Right subarray
int j = 0;
// Initial index of merged subarray
int k = leftIndex;
while (i < leftSubarraySize && j < rightSubarraySize)
{
if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in L[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (i < leftSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in R[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (j < rightSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
void mergeSort(int arr[], int leftIndex, int rightIndex)
{
if(leftIndex >= rightIndex)
{
return;
}
int middleIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex - leftIndex)/2;
mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex);
mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex);
merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex);
}
// Function to print the elements
// of the array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Unsorted array:" << endl;
printArray(arr, size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, size - 1);
cout << "Sorted array:" << endl;
printArray(arr, size);
return 0;
}Producción:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19Implementación de JavaScript del algoritmo de ordenación por fusión
A continuación se muestra la implementación de JavaScript del algoritmo de ordenación por combinación:
// JavaScript implementation of the
// merge sort algorithm
// This function merges two subarrays of arr[]
// Left subarray: arr[leftIndex..middleIndex]
// Right subarray: arr[middleIndex+1..rightIndex]
function merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex) {
let leftSubarraySize = middleIndex - leftIndex + 1;
let rightSubarraySize = rightIndex - middleIndex;
// Create temporary arrays
var L = new Array(leftSubarraySize);
var R = new Array(rightSubarraySize);
// Copying data to temporary arrays L[] and R[]
for(let i = 0; i<leftSubarraySize; i++) {
L[i] = arr[leftIndex + i];
}
for (let j = 0; j<rightSubarraySize; j++) {
R[j] = arr[middleIndex + 1 + j];
}
// Merge the temporary arrays back into arr[leftIndex..rightIndex]
// Initial index of Left subarray
var i = 0;
// Initial index of Right subarray
var j = 0;
// Initial index of merged subarray
var k = leftIndex;
while (i < leftSubarraySize && j < rightSubarraySize)
{
if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in L[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (i < leftSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in R[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (j < rightSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
function mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, rightIndex) {
if(leftIndex >= rightIndex) {
return
}
var middleIndex = leftIndex + parseInt((rightIndex - leftIndex)/2);
mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex);
mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex);
merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex);
}
// Function to print the elements
// of the array
function printArray(arr, size) {
for(let i = 0; i<size; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Driver code:
var arr = [ 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 ];
var size = arr.length;
document.write("Unsorted array:<br>");
printArray(arr, size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, size - 1);
document.write("Sorted array:<br>");
printArray(arr, size);Producción:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19
Implementación en Python del algoritmo de clasificación por fusión
A continuación se muestra la implementación de Python del algoritmo de clasificación de combinación:
# Python implementation of the
# merge sort algorithm
def mergeSort(arr):
if len(arr) > 1:
# Finding the middle index of the array
middleIndex = len(arr)//2
# Left half of the array
L = arr[:middleIndex]
# Right half of the array
R = arr[middleIndex:]
# Sorting the first half of the array
mergeSort(L)
# Sorting the second half of the array
mergeSort(R)
# Initial index of Left subarray
i = 0
# Initial index of Right subarray
j = 0
# Initial index of merged subarray
k = 0
# Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[]
while i < len(L) and j < len(R):
if L[i] < R[j]:
arr[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
else:
arr[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
k = k + 1
# Checking if there're some remaining elements
while i < len(L):
arr[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
k = k + 1
while j < len(R):
arr[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
k = k + 1
# Function to print the elements
# of the array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
print()
# Driver code
arr = [ 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 ]
size = len(arr)
print("Unsorted array:")
printArray(arr, size)
mergeSort(arr)
print("Sorted array:")
printArray(arr, size)
Producción:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19Comprender otros algoritmos de clasificación
La clasificación es uno de los algoritmos más utilizados en programación. Puede ordenar elementos en diferentes lenguajes de programación utilizando varios algoritmos de clasificación como clasificación rápida, clasificación de burbujas, clasificación de combinación, clasificación de inserción, etc.
La clasificación de burbujas es la mejor opción si desea aprender sobre el algoritmo de clasificación más simple.
